3D Optical Waveguides
Holographic photopolymers can be cast onto and around other optical elements, then patterned with a 3D routed waveguide to form hybrid integrated photonics. While multi-photon initiation can be used to improve localization of the written feature, we have explored single-photon initiation due to its greater control at lower laser power and higher write speed. For example, a milliwatt laser focus translated through the 3D volume of a holographic photopolymer writes an optical waveguide with a cross section related to the size, shape, speed and velocity of the laser focus. These variables allow the waveguide to be arbitrarily routed, tapered and shaped along its path to implement mode transformations between encapsulated subcomponents. We have also created intererence lithography systems capable of creating large 2D arrays of parallel waveguides and 3D printers that can fabricate arbitrary waveguide arrays layer by layer.
The team
- Davig Glugla
- Amy Sullivan
- Cotton Anderson
Learn more
- D. J. Glugla, M. B. Chosy, M. D. Alim, A. C. Sullivan, R. R. McLeod, “Transport-of-Intensity-Based Phase Imaging to Quantify the Refractive Index Response of 3D Direct-Write Lithography,” Optics Express 26, pp. 1851-1869, 2018
- C. Ye, K. T. Kamysiak, A. C. Sullivan, R. R. McLeod, Mode profile imaging and loss measurement for uniform and tapered single-mode 3D waveguides in diffusive-based photopolymer, Optics Express 20, 6575-6583, 2012.
- A. C. Sullivan, M. W. Grabowski, R. R. McLeod, Three-dimensional direct-write lithography into photopolymer, Applied Optics 46, 295-301, 2007.
- Amy C. Sullivan, Doctor of Philosophy in Physics, Tomographic Characterization of Volume Photopolymers for Integrated Optics, University of Colorado, 2008.
- Charles D. Anderson, Master of Science in Electrical Engineering, Photopolymer waveguide to fiber coupling via 3D direct-write lithography, University of Colorado, 2006.
This work has been generously funded by





Sample results
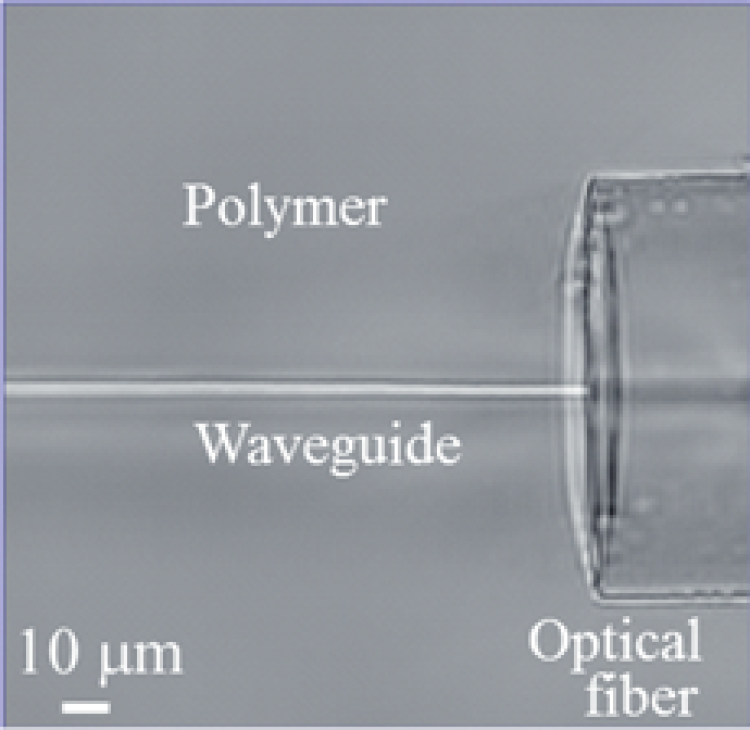
Phase micrograph of a single mode optical fiber encapsulated in solid holographic photopolymer and subsequently connected to an optical waveguide written with 3D laser direct write lithography.
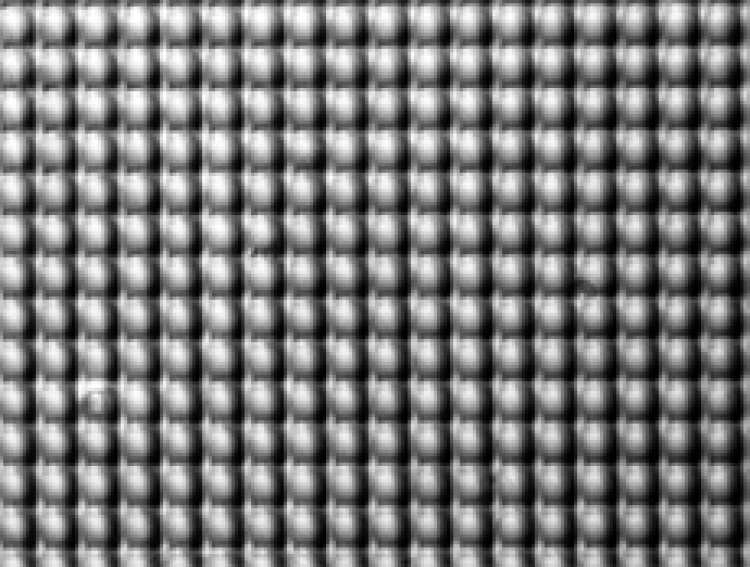
Differential interference contrast micrograph of a photopolymer waveguide array written into a 3D photopolymer with four beam, phase stabilized interference lithography. While the DIC microscope renders this as what appears to be a bumpy sheet, the polmer surface is flat.
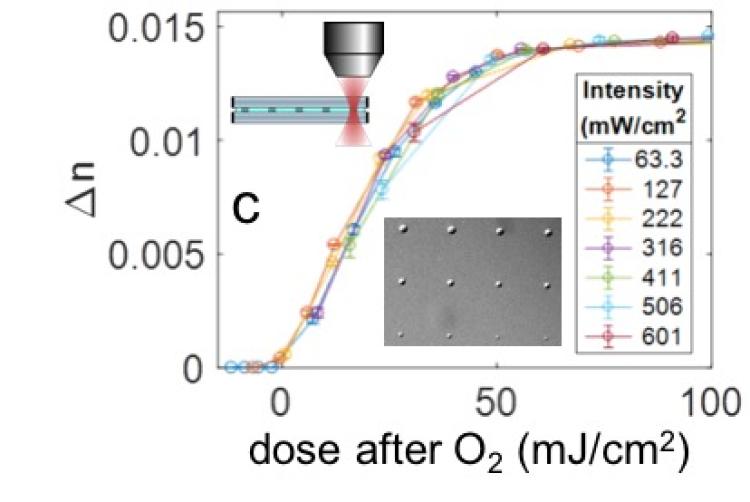
Laser direct write plus quantitative phase metrology used to acuratly characterize the index response of a holographic photopolymer at the micron scale.


