Atomistic Hydrodynamics and the Dynamical Hydrophobic Effect in Porous Graphene
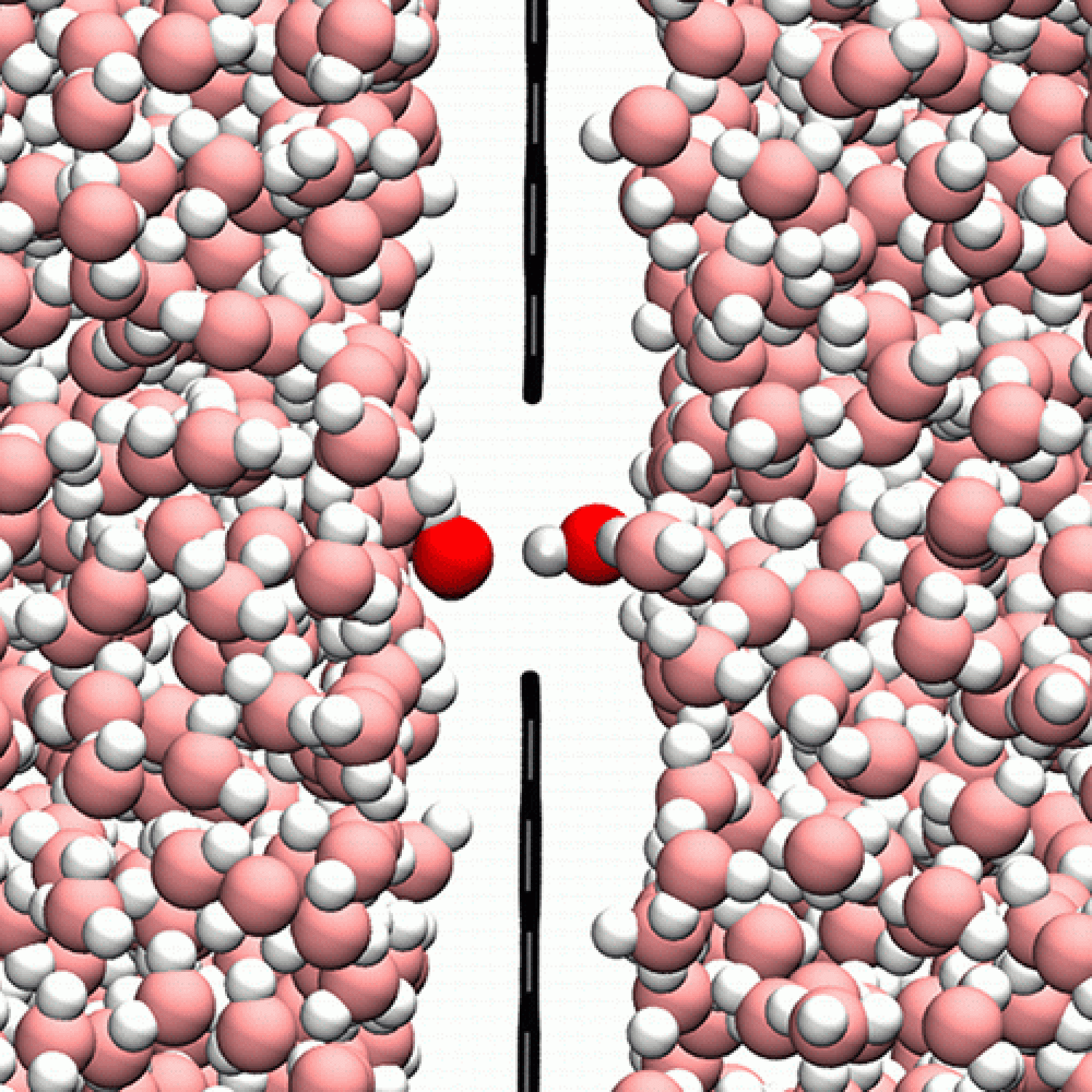
Mirroring their role in electrical and optical physics, two-dimensional crystals are emerging as novel platforms for fluid separations and water desalination, which are hydrodynamic processes that occur in nanoscale environments. For numerical simulation to play a predictive and descriptive role, one must have theoretically sound methods that span orders of magnitude in physical scales, from the atomistic motions of particles inside the channels to the large-scale hydrodynamic gradients that drive transport. Here, we use constraint dynamics to derive a nonequilibrium molecular dynamics method for simulating steady-state mass flow of a fluid moving through the nanoscopic spaces of a porous solid. After validating our method on a model system, we use it to study the hydrophobic effect of water moving through pores of electrically doped single-layer graphene. The trend in permeability that we calculate does not follow the hydrophobicity of the membrane but is instead governed by a crossover between two competing molecular transport mechanisms.
Strong, S. E. and Eaves, J. D., Atomistic Hydrodynamics and the Dynamical Hydrophobic Effect in Porous Graphene. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 1907 (2016)

