Nanocrystalline Iron Monosulfides Near Stoichiometry
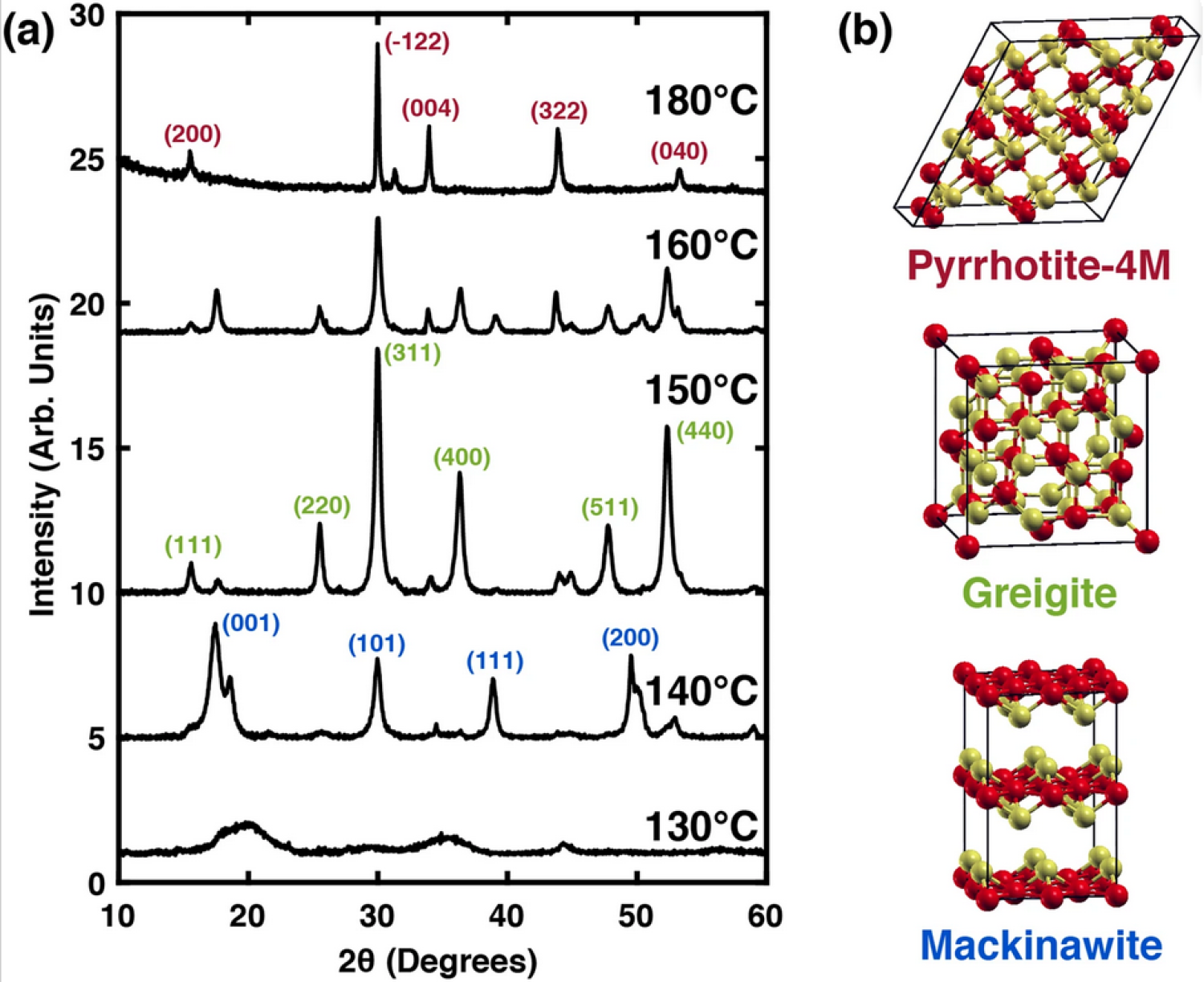
Solids composed of iron and sulfur are earth abundant and nontoxic, and can exhibit interesting and technologically important optical, electronic, and magnetic phenomena. However, the iron-sulfur (Fe-S) phase diagram is congested in regions of slight non-stoichiometric iron vacancies, and even when the iron atomic composition changes by even a few percent at standard temperature and pressure, there are myriad stable crystal phases that form with qualitatively different electronic properties. Here, we synthesized and characterized nanocrystals of the pyrrhotite-4M structure (Fe7S8) in an anhydrous oleylamine solvent. Upon heating from 140 °C to 180 °C, the solid sequentially transformed into two kinetically trapped FeS intermediate phases before reaching the pyrrhotite-4M final product. Finally, we assessed the effects of iron vacancies using the stoichiometric end-member, troilite, as a reference system. Density functional theory calculations show that iron vacancies in troilite shift the structure from hexagonal FeS to a monoclinic structure, similar to crystal structures of pyrrhotites, and suggest that this iron deficient troilite may be a stable intermediate between the two crystal structures. The calculations predict that defects also close the band gap in iron deficient troilite.
Roberts, D. E.*, Landin, A. R.*, Ritter, T. G., Eaves, J. D., and Stoldt C. R., Nanocrystalline Iron Monosulfides Near Stoichiometry. Sci. Rep. 8, 6591 (2018)
* These authors contributed equally to this work

