Multimodal Nonlinear Optical Microscopy
Includes Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering (CARS), multi-photon excited (MPE) fluorescence, and second/third harmonic generation (SHG/THG) microscopy.


Layered structure depth profile images of liquid crystal samples between two cover slips obtained by the three photon excited fluorescence technique.
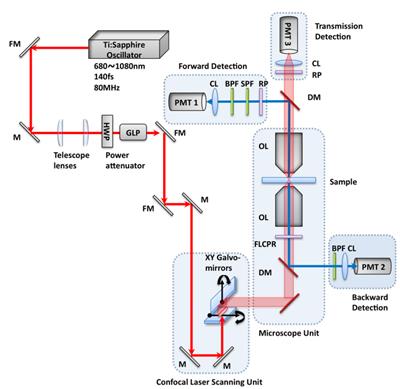
Experimental setup for the multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy of multiphoton excitation fluorescence (MPEF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging. A femtosecond pulse from a tunable Ti:Sapphire oscillator (680~1080nm, 140fs, 80MHz, Chameleon Ultra II, Coherent Inc.) is introduced into a confocal laser scanning unit (Fluoview FV-300, Olympus Inc.) and focused onto a sample with a high NA objective lens of an inverted microscope (IX-81, Olympus Inc.). The half wave plate and the Glan-laser polarizer allow control of power and polarization. Two or three photon excitation fluorescence, second harmonic signals and transmission light can be collected by three different detection channels with photon multiplier tubes (H5784-20, Hamamatsu), i.e. forward, backward, or transmission detection systems. The polarization at sample position can be controlled by using a ferroelectric liquid crystal polarization rotator, which changes polarization direction by applying a different voltage. [CL: collecting lens, DM: dichroic mirror, FLCPR: ferroelectric liquid crystal polarization rotator, FM: flip mirror, GLP: Glan laser polarizer, HWP: broadband half wave plate, LPF: long pass filter, M: mirror, OL: objective lens, RP: rotating polarizer, SPF: short pass filter].
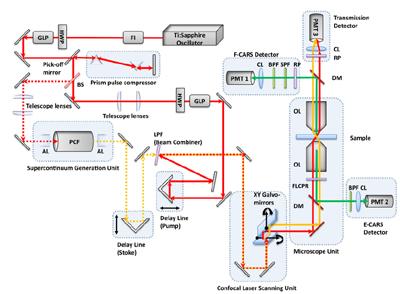
Experimental setup for the multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy of multiphoton excitation fluorescence (MPEF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging. A femtosecond pulse from a tunable Ti:Sapphire oscillator (680~1080nm, 140fs, 80MHz, Chameleon Ultra II, Coherent Inc.) is introduced into a confocal laser scanning unit (Fluoview FV-300, Olympus Inc.) and focused onto a sample with a high NA objective lens of an inverted microscope (IX-81, Olympus Inc.). The half wave plate and the Glan-laser polarizer allow control of power and polarization. Two or three photon excitation fluorescence, second harmonic signals and transmission light can be collected by three different detection channels with photon multiplier tubes (H5784-20, Hamamatsu), i.e. forward, backward, or transmission detection systems. The polarization at sample position can be controlled by using a ferroelectric liquid crystal polarization rotator, which changes polarization direction by applying a different voltage. [CL: collecting lens, DM: dichroic mirror, FLCPR: ferroelectric liquid crystal polarization rotator, FM: flip mirror, GLP: Glan laser polarizer, HWP: broadband half wave plate, LPF: long pass filter, M: mirror, OL: objective lens, RP: rotating polarizer, SPF: short pass filter].

Taewoo Lee and Rahul Trivedi aligning optical beam paths from a femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser for CARS imaging.

