paper
 Many soft-matter and biophysical systems are composed of monomers that reversibly assemble into rod-like aggregates that can then order into liquid-crystal phases.
Many soft-matter and biophysical systems are composed of monomers that reversibly assemble into rod-like aggregates that can then order into liquid-crystal phases.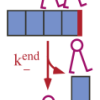 Proteins from the kinesin-8 family promote microtubule depolymerization, a process thought to be important for the control of microtubule length in living cells.
Proteins from the kinesin-8 family promote microtubule depolymerization, a process thought to be important for the control of microtubule length in living cells.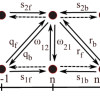 Helicases are molecular motors that unwind double-stranded nucleic acids. Here we model a helicase motor that can switch between two states, which could represent two different points in the ATP hydrolysis cycle.
Helicases are molecular motors that unwind double-stranded nucleic acids. Here we model a helicase motor that can switch between two states, which could represent two different points in the ATP hydrolysis cycle.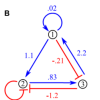 The balance between activating and inhibiting connections is important in determining whether network dynamics reach steady state or oscillate.
The balance between activating and inhibiting connections is important in determining whether network dynamics reach steady state or oscillate. TFIIA induces a conformational change within the TBP/TATA complex that enhances its stability under both in vitro and physiological salt conditions. We present a refined model for the effect that TFIIA has on DNA conformation that takes into account potential changes in bend angle as well as twist angle.
TFIIA induces a conformational change within the TBP/TATA complex that enhances its stability under both in vitro and physiological salt conditions. We present a refined model for the effect that TFIIA has on DNA conformation that takes into account potential changes in bend angle as well as twist angle. The wormlike chain (WLC) model currently provides the best description of double-stranded DNA elasticity for micron-sized molecules.
The wormlike chain (WLC) model currently provides the best description of double-stranded DNA elasticity for micron-sized molecules.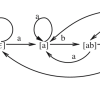 RNA motifs typically consist of short, modular patterns that include base pairs formed within and between modules. Estimating the abundance of these patterns is of fundamental importance.
RNA motifs typically consist of short, modular patterns that include base pairs formed within and between modules. Estimating the abundance of these patterns is of fundamental importance.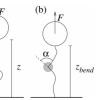 Single-molecule experiments have studied the elasticity of DNA with helix-deforming proteins, including proteins that bend DNA, using relatively short DNA molecules with a single, well-defined bend site. We developed a simple, theoretical description of the effect of a single bend.
Single-molecule experiments have studied the elasticity of DNA with helix-deforming proteins, including proteins that bend DNA, using relatively short DNA molecules with a single, well-defined bend site. We developed a simple, theoretical description of the effect of a single bend. To investigate the mechanisms of Smad nuclear accumulation, we developed a simple mathematical model of canonical Smad signalling.
To investigate the mechanisms of Smad nuclear accumulation, we developed a simple mathematical model of canonical Smad signalling.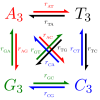 Horizontal gene transfer has allowed bacteria to evolve many new capabilities. We introduce a new class of methods for detecting HGT based on the changes in nucleotide substitution rates.
Horizontal gene transfer has allowed bacteria to evolve many new capabilities. We introduce a new class of methods for detecting HGT based on the changes in nucleotide substitution rates.

