cam
 Toward task capable active matter: learning to avoid clogging in confined collectives via collisionsA robotic excavating swarm with simple learning rules can mitigate jams.
Toward task capable active matter: learning to avoid clogging in confined collectives via collisionsA robotic excavating swarm with simple learning rules can mitigate jams.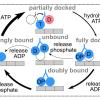 We describe a new simulation framework for motor protein and crosslinker interaction with microtubules in a lattice model.
We describe a new simulation framework for motor protein and crosslinker interaction with microtubules in a lattice model.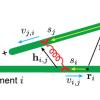 We explore different types of analytic models for crosslinkers and compare them to simulation.
We explore different types of analytic models for crosslinkers and compare them to simulation.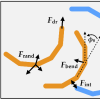 We present Brownian dynamics simulation results of driven semiflexible filaments with intrinsic curvature and investigate how the interplay between filament rigidity and radius of curvature can tune the self-organization behavior in homochiral systems and heterochiral mixtures.
We present Brownian dynamics simulation results of driven semiflexible filaments with intrinsic curvature and investigate how the interplay between filament rigidity and radius of curvature can tune the self-organization behavior in homochiral systems and heterochiral mixtures. We use simulations of driven filaments with tunable soft repulsion and rigidity in order to better understand how the interplay between filament flexibility and steric effects can lead to different active steady states.
We use simulations of driven filaments with tunable soft repulsion and rigidity in order to better understand how the interplay between filament flexibility and steric effects can lead to different active steady states.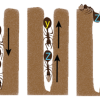 Groups of interacting active particles, insects, or humans can form clusters that hinder the goals of the collective. We find that digging performance can be robustly optimized within the constraints of narrow tunnels by individual idleness and retreating.
Groups of interacting active particles, insects, or humans can form clusters that hinder the goals of the collective. We find that digging performance can be robustly optimized within the constraints of narrow tunnels by individual idleness and retreating.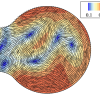 Our paper "Analytical structure, dynamics, and coarse-graining of a kinetic model of an active fluid" was published by Physical Review Fluids.
Our paper "Analytical structure, dynamics, and coarse-graining of a kinetic model of an active fluid" was published by Physical Review Fluids.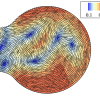 Our paper "Analytical structure, dynamics, and coarse-graining of a kinetic model of an active fluid" was posted on the arXiv preprint server today.
Our paper "Analytical structure, dynamics, and coarse-graining of a kinetic model of an active fluid" was posted on the arXiv preprint server today.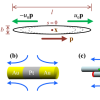 One of the simplest active suspensions with complex dynamics is a suspension of immotile "Extensor" particles that exert active extensile dipolar stresses on the fluid in which they are immersed.
One of the simplest active suspensions with complex dynamics is a suspension of immotile "Extensor" particles that exert active extensile dipolar stresses on the fluid in which they are immersed. We study a physical model of filaments, crosslinking motors, and static crosslinkers to dissect the microscopic mechanisms of active stress generation in a two-dimensional system of orientationally aligned rods.
We study a physical model of filaments, crosslinking motors, and static crosslinkers to dissect the microscopic mechanisms of active stress generation in a two-dimensional system of orientationally aligned rods.

