Phase-plane analysis of the totally asymmetric simple exclusion process with binding kinetics and switching between antiparallel lanes
Hui-Shun Kuan and Meredith D. Betterton (2016). Physical Review E94, 022419. arXiv:1604.00690. Download.
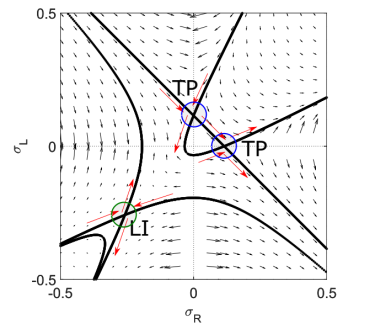
Motor protein motion on biopolymers can be described by models related to the totally asymmetric simple exclusion process (TASEP). Inspired by experiments on the motion of kinesin-4 motors on antiparallel microtubule overlaps, we analyze a model incorporating the TASEP on two antiparallel lanes with binding kinetics and lane switching. We determine the steady-state motor density profiles using phase plane analysis of the steady-state mean field equations and kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. We focus on the the density-density phase plane, where we find an analytic solution to the mean-field model. By studying the phase space flows, we determine the model’s fixed points and their changes with parameters. Phases previously identified for the single-lane model occur for low switching rate between lanes. We predict a new multiple coexistence phase due to additional fixed points that appear as the switching rate increases: switching moves motors from the higher-density to the lower-density lane, causing local jamming and creating multiple domain walls. We determine the phase diagram of the model for both symmetric and general boundary conditions.

